Ever noticed how our digital world thrives on seamless connectivity? At the core of this intricate dance of data lies switches, the unsung heroes of networking. From sprawling enterprises to small home offices, the type of switch deployed can dramatically impact network performance and efficiency.
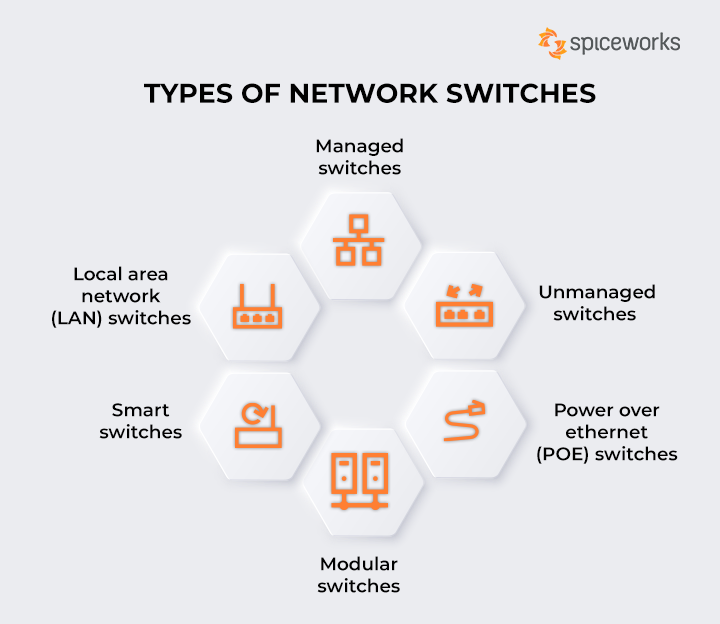
Historically, the four primary types of switches include unmanaged, managed, smart, and PoE (Power over Ethernet) switches. While unmanaged switches offer simplicity and affordability, managed switches provide robust control and monitoring capabilities. Smart switches strike a balance with partial manageability, whereas PoE switches conveniently power devices like IP cameras and phones, saving time and cabling costs.

What are the Four Types of Switches in Networking
Unmanaged switches are the simplest type, often used in small networks. They require no configuration and offer basic connectivity. They are cost-effective and ideal for home or small office setups. While they lack advanced features, their plug-and-play nature makes them user-friendly. However, they don’t offer control over network traffic.
Managed switches provide more control and flexibility. They allow network administrators to configure, manage, and monitor the network. These switches offer features like VLANs, Quality of Service (QoS), and SNMP. They are suitable for larger networks with complex requirements. The ability to troubleshoot and optimize performance makes them essential for enterprise environments.
Smart switches, also known as web-managed switches, strike a balance between unmanaged and managed switches. They offer basic management options through a simple web interface. They are more affordable than fully managed switches but provide more features than unmanaged ones. Enterprises often use them in smaller networks or edge applications. With limited but essential controls, they are easy to set up and manage.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) switches not only connect devices but also supply power through the same Ethernet cable. This feature is useful for devices like IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points. PoE switches reduce the need for additional power sources and cables. They are commonly used in environments requiring centralized power management. These switches simplify installation and enhance flexibility.
Unmanaged Switches
Unmanaged switches are a straightforward solution for networking needs, especially in small environments. They come ready to use right out of the box, with no need for configuration. This simplicity makes them perfect for home networks or small offices. Users can just plug in their devices and start sharing resources immediately. Despite their basic functionality, they are reliable for everyday use.
These switches are also cost-effective, making them an attractive option for those on a budget. They provide the necessary connectivity without the extra features that drive up the cost. Small businesses often choose unmanaged switches to save money while still maintaining network effectiveness. This makes them a useful, budget-friendly tool in various settings. However, the lack of advanced features can be a limitation in more complex networks.
Even though unmanaged switches lack the advanced features of their managed counterparts, they still offer a few essential benefits. They are incredibly easy to set up, requiring no technical expertise. This ease of use makes them ideal for non-technical users. Additionally, their compact size allows for easy placement in tight spaces. Unmanaged switches are practical and meet basic network needs efficiently.
These switches are designed to handle basic tasks like connecting computers, printers, and other devices. Due to their limited functionality, they are less versatile than managed or smart switches. They don’t support advanced features like VLANs or Quality of Service (QoS). Consequently, they are not the best choice for larger networks with specific requirements. For simple, low-maintenance networks, unmanaged switches are a solid choice.
Managed Switches
Managed switches offer extensive control over your network, making them ideal for larger organizations. They allow network administrators to configure settings, monitor traffic, and create virtual LANs (VLANs). These features enhance network efficiency and security. Managed switches also support advanced functions like Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize certain types of data. They provide detailed insights into network performance, aiding in troubleshooting.
The flexibility of managed switches is another major advantage. They can be customized to fit specific network requirements, adapting to various operational needs. This adaptability makes them suitable for different environments, from data centers to enterprise networks. Organizations can manage bandwidth more effectively, ensuring smooth performance. Enhanced security features protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. This makes managed switches crucial for complex and dynamic networks.
Despite their higher cost, managed switches provide excellent long-term value. Their advanced features justify the investment as they offer greater control and optimization of network resources. Companies often find that the initial expense is balanced by the improved performance and security. Managed switches can also scale with your growing network needs. This scalability makes them a future-proof solution for many businesses.
Some common features of managed switches include:
- Port Mirroring
- Layer 3 Routing
- Network Redundancy
- Remote Management Capabilities
- SNMP Support for Network Monitoring
These features are not commonly found in unmanaged or smart switches, setting managed switches apart in terms of capability and control.
Smart Switches
Smart switches, also known as web-managed switches, occupy a middle ground between unmanaged and managed switches. They offer basic network management features via a simple web interface. This makes them easier to use than fully managed switches, while still providing more control than unmanaged ones. They are suitable for small to medium-sized networks that require some level of management. Smart switches are often used in branch offices or smaller enterprise networks.
One of the key features of smart switches is their affordability. While they are more expensive than unmanaged switches, they are less costly than fully managed switches. This makes them a budget-friendly option for businesses needing some network management capabilities. Despite their lower cost, they still offer essential features like VLAN support and port monitoring. This balance between cost and functionality makes them popular.
Smart switches provide a user-friendly interface that simplifies network configuration. Administrators can easily set up and manage VLANs, monitor network traffic, and configure basic security settings. The straightforward web-based interface does not require extensive technical knowledge. This makes smart switches accessible to users who may not be networking experts. Ease of use is a significant advantage of smart switches.
The versatility of smart switches makes them adaptable to different environments. They can be used in various settings, from corporate offices to educational institutions. They offer enough control to enhance network performance without the complexity of fully managed switches. This makes them ideal for networks that need moderate management capabilities. They provide a balance that meets most organizational needs.
Here are some common features found in smart switches:
- Basic VLAN Configuration
- Link Aggregation
- Port Monitoring
- Quality of Service (QoS)
These features help improve network efficiency and manageability, making smart switches a practical choice for many users.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) Switches
Power over Ethernet (PoE) switches offer the unique ability to transmit both data and electrical power over the same Ethernet cable. This feature eliminates the need for separate power cords, simplifying cable management. PoE switches are particularly useful for devices like IP cameras, Wi-Fi access points, and VoIP phones. They make installation easier and more efficient, especially in places where power sources are limited. This reduces the complexity and cost of network setups.
Another advantage of PoE switches is their ability to centralize power management. By providing power through the network, these switches allow for centralized control over various devices. This means you can easily reset or shut down devices remotely. Centralized power also helps in troubleshooting and maintaining the network. It ensures a more streamlined and efficient management process.
PoE switches come in two main types: standard PoE and PoE+. Standard PoE can deliver up to 15.4 watts of power per port, while PoE+ can provide up to 30 watts. The additional power capacity of PoE+ is beneficial for devices that require more electricity. Choosing between the two depends on the specific power needs of your network devices. Understanding these differences can help in selecting the most appropriate type of PoE switch.
Here are some key benefits of PoE switches:
- Simplified installation process
- Centralized power management
- Support for various PoE-powered devices
- Cost and time-saving in cabling
PoE switches are versatile and can be used in various settings, from corporate offices to industrial environments. They offer a practical solution for networks requiring both data and power connections. This makes them a valuable addition to modern networking setups.
Factors to Consider when Choosing Networking Switches
When selecting a networking switch, the size of your network is a crucial factor. For small home networks, an unmanaged switch might be sufficient. However, larger networks may require the advanced features of managed or smart switches. It’s important to assess the number of devices that will connect to the switch. This helps in determining the required number of ports.
Bandwidth requirements also play a significant role in choosing the right switch. Networks that handle heavy traffic or multiple data streams benefit from switches that support higher speeds. Features like link aggregation can combine multiple connections for increased bandwidth. This ensures efficient data transmission and prevents bottlenecks. Knowing your bandwidth needs can guide you toward the best switch option.
Another essential factor is network management capabilities. Managed switches offer more control and monitoring options compared to unmanaged or smart switches. These features are beneficial for troubleshooting and optimizing network performance. Advanced settings like VLANs, Quality of Service (QoS), and SNMP support provide greater flexibility. If network control is a priority, a managed switch would be the best choice.
Security features should not be overlooked when choosing a switch. Managed switches often come with robust security options to protect the network. Features like port security, access control lists, and encryption can safeguard data. For networks handling sensitive information, these security measures are vital. Ensuring the switch has adequate security features is essential for data protection.
Here are some key factors to consider:
- Number of Ports
- Network Size
- Bandwidth Requirements
- Management Capabilities
- Security Features
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make an informed decision when selecting a networking switch. This ensures that the switch will meet your network’s specific needs and enhance its performance.
The Role of Switches in Network Design
Switches are vital components in network design, acting as the central hub for connecting devices. They forward data to its destination by using MAC addresses to direct traffic efficiently. This ensures smooth communication within the network and prevents data collisions. In larger networks, switches can segment traffic to improve performance. With these capabilities, they play a fundamental role in maintaining network efficiency.
One key role of switches is enhancing network scalability. As organizations grow, their networking needs become more complex. Switches support this growth by allowing easy expansion without disrupting existing operations. Managed switches, in particular, can be configured to support new devices and users seamlessly. This flexibility helps networks adapt to changing demands.
Switches also contribute significantly to network security. Advanced features like VLANs isolate different segments of the network for better control and protection. Managed switches offer security protocols that monitor and restrict access to sensitive data. These capabilities are essential for safeguarding against unauthorized access and cyber threats. By implementing robust security measures, switches help maintain the integrity of the network.
- Efficient Data Forwarding
- Network Scalability
- Enhanced Security
- Performance Optimization
In terms of performance optimization, switches manage data flow to prevent congestion and ensure reliable connectivity. Features like Quality of Service (QoS) prioritize critical data transmissions over less important traffic. This ensures that essential applications run smoothly even during high-traffic periods. Effective use of QoS enhances overall user experience.
Another important aspect is the customization offered by managed and smart switches. These switches allow administrators to personalize settings based on specific requirements such as bandwidth allocation or port configuration. Customization provides greater control over how data travels through the network, optimizing both speed and reliability.
Distinguishing Factors Between Four Types of Switches
Understanding the key differences between unmanaged, managed, smart, and Power over Ethernet (PoE) switches is essential for making an informed decision. Unmanaged switches are the simplest, offering plug-and-play functionality without any configuration options. This makes them ideal for small networks with straightforward communication needs. They are cost-effective but lack advanced features like monitoring and control. Their simplicity is both an advantage and a limitation.
Managed switches, on the other hand, provide extensive control over network settings. They offer features such as VLANs, Quality of Service (QoS), and port mirroring. Managed switches are suitable for large or complex networks requiring detailed monitoring and fine-tuned performance. They are more expensive than unmanaged switches due to their robust capabilities. However, the investment is often justified by the greater network control and security they provide.
Smart switches strike a balance between unmanaged and managed switches. They come with a web-based interface that allows for basic configuration and monitoring. Smart switches are more affordable than fully managed switches but offer more control than unmanaged ones. They are ideal for small to medium-sized networks needing moderate customization and monitoring. This makes them a good choice for users seeking a middle ground.
PoE switches add another layer of functionality by providing both data and electrical power through the same Ethernet cable. This dual capability simplifies installations for devices such as IP cameras, Wi-Fi access points, and VoIP phones. PoE switches eliminate the need for separate power sources, reducing clutter and installation costs. They are particularly useful in environments where running power cables is challenging. Their versatility and convenience set them apart from other types of switches.
- Unmanaged Switches: Simple, low-cost, no configuration
- Managed Switches: Extensive control, monitoring, higher cost
- Smart Switches: Web interface, moderate control, balanced cost
- PoE Switches: Power and data over one cable, simplifies installations
Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right switch for your network needs. By evaluating factors like network size, budget, and desired level of control, you can select the most appropriate switch type. Each type has its unique advantages, making it suitable for specific situations and requirements.
Future of Networking Switches
Advancements in network technology are making switches smarter and more efficient. The future will likely see more integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning in switches. These technologies can help automate network management, identify patterns, and predict issues before they arise. This proactive approach will make networks more reliable and reduce downtime. As a result, businesses will benefit from increased productivity.
Another emerging trend is the development of cloud-managed switches. These switches allow administrators to manage the network remotely via a cloud-based platform. This remote management capability is convenient for enterprises with multiple locations. It also simplifies the process of updating and securing the network. Cloud-managed switches offer flexibility and ease of use, making them an attractive option for the future.
Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on energy efficiency in network switches. Manufacturers are designing switches that consume less power while maintaining high performance. This is crucial for reducing operational costs and minimizing environmental impact. Green networking practices will become more prevalent as businesses prioritize sustainability. Energy-efficient switches will play a significant role in this shift.
Here are some key factors driving the future of networking switches:
- Integration of AI and machine learning
- Cloud-managed switches
- Focus on energy efficiency
- Enhanced security features
Switches with enhanced security features will also be essential in the future. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, the need for robust security measures increases. Future switches will likely offer advanced encryption, intrusion detection, and automated threat response. These features will help protect sensitive data and ensure network integrity. Emphasizing security will be critical for the evolving landscape of networking.
Another area of growth is the increased use of high-speed switches to support faster data transmission. With the rise of 5G and other high-speed networks, switches capable of handling higher data rates will be in demand. These high-speed switches will ensure smooth and efficient data flow, meeting the needs of modern applications. Faster speeds will greatly enhance user experiences and network performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Networking switches play a crucial role in managing data flow within local area networks (LANs). Here are some frequently asked questions to help you understand them better.
1. How do unmanaged switches differ from managed switches?
Unmanaged switches are plug-and-play devices that require no configuration, making them easy to set up. They are ideal for small networks with simple needs but lack advanced features like network monitoring and traffic management.
Managed switches, on the other hand, offer extensive control and customization options. They provide features such as VLAN support, Quality of Service (QoS), and remote management, making them suitable for larger or more complex networks.
2. What is the purpose of a smart switch in a network?
A smart switch bridges the gap between unmanaged and managed switches by offering basic management capabilities through a web interface. It provides limited but essential control over things like VLAN settings and port configurations without requiring complicated setup processes.
This makes smart switches suitable for small to medium-sized businesses that need more than an unmanaged switch but don’t require all the features of a fully managed switch. It offers a balance between functionality and ease of use.
3. Why would you choose a PoE switch over other types?
A Power over Ethernet (PoE) switch can transmit both data and electrical power through a single Ethernet cable, simplifying device installations. This is particularly useful for devices like IP cameras, Wi-Fi access points, and VoIP phones that are often installed where power outlets are not readily available.
PoE switches reduce the need for separate power supplies or additional cabling, cutting down on installation costs and complexity. They’re ideal for environments where centralized power management is beneficial.
4. What are the security benefits of using managed switches?
Managed switches offer enhanced security features compared to unmanaged or smart switches. They can support advanced security protocols such as access control lists (ACLs), port security, and 802.1X authentication to protect against unauthorized access.
This level of control allows network administrators to create secure segments within the network while monitoring suspicious activity effectively. Managed switches help safeguard sensitive data from potential threats.
5. Can smart switches handle heavy network traffic efficiently?
While smart switches offer basic configuration options aimed at improving network efficiency, they might not be as capable as fully managed switches when handling very high volumes of traffic. Smart switches include QoS features that prioritize certain types of data but come with limited advanced functionalities.
This makes them adequate for moderate use cases but less effective under demanding conditions with numerous users or applications needing high bandwidth simultaneously.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of network switches is essential for optimizing any network. Each type—unmanaged, managed, smart, and PoE—offers unique benefits and features tailored to specific needs. Unmanaged switches provide simplicity, while managed switches offer extensive control. Smart switches strike a balance, and PoE switches add the convenience of power delivery.
Choosing the right switch depends on the size, complexity, and specific requirements of your network. Consider factors like network management, security, and scalability to make an informed decision. With the right switch, you can enhance performance and ensure reliable connectivity. Investing in the appropriate switch adds long-term value to your network infrastructure.



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.